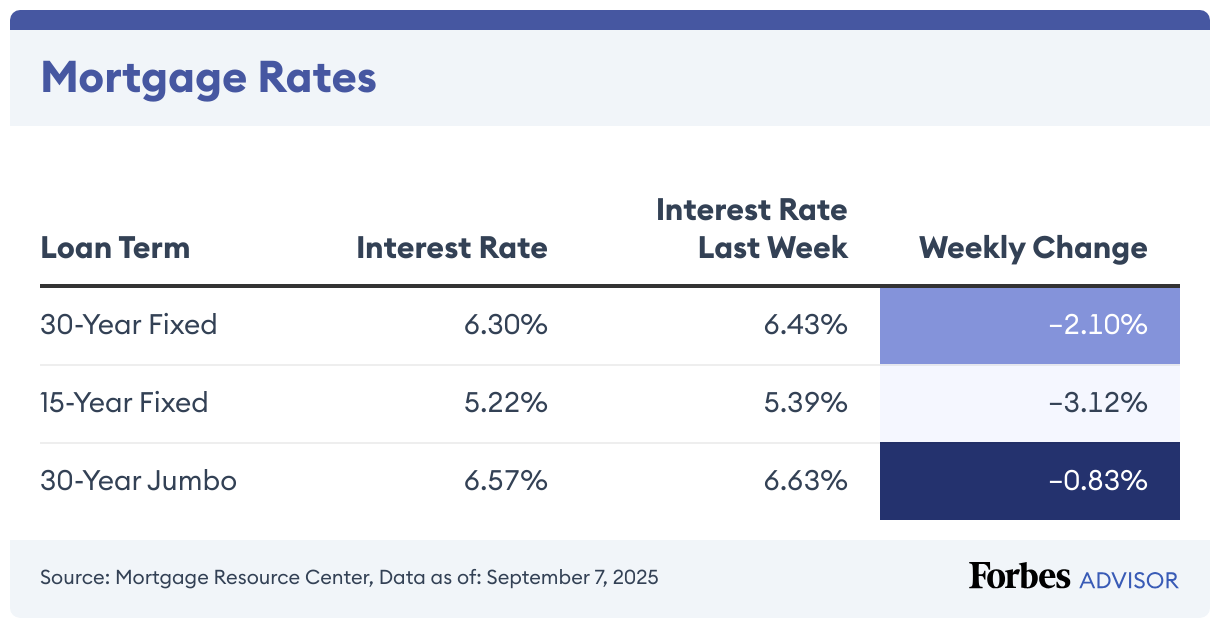
The current average mortgage rate on a 30-year fixed mortgage is 6.34%, according to the Mortgage Research Center. The average rate on a 15-year mortgage is 5.40%, while the average rate on a 30-year jumbo mortgage is 6.67%.
30-Year Mortgage Rates Drop 0.24%
Today, the average rate on a 30-year mortgage is 6.34%, compared to last week when it was 6.35%.
The APR on a 30-year, fixed-rate mortgage is 6.37%. The APR was 6.38% last week. APR is the all-in cost of your loan.
With today’s interest rate of 6.34%, a 30-year fixed mortgage of $100,000 costs approximately $621 per month in principal and interest (taxes and fees not included), the Forbes Advisor mortgage calculator shows. Borrowers will pay about $124,428 in total interest over the life of the loan.
15-Year Mortgage Rates Remain Steady
Today, the 15-year mortgage rate is 5.4%, the same as it was yesterday. Last week, it was 5.4%.
On a 15-year fixed, the APR is 5.44%. Last week it was 5.44%.
A 15-year fixed-rate mortgage of $100,000 with today’s interest rate of 5.4% will cost $812 per month in principal and interest. Over the life of the loan, you would pay $46,541 in total interest.
Jumbo Mortgage Rates Drop 0.49%
Today’s average interest rate on a 30-year fixed-rate jumbo mortgage (a mortgage above 2025’s conforming loan limit of $806,500 in most areas) fell 0.49% from last week to 6.67%.
Borrowers with a 30-year, fixed-rate jumbo mortgage with today’s interest rate of 6.67% will pay approximately $643 per month in principal and interest per $100,000 borrowed. That would be $131,942.
Trends in Mortgage Rates for 2025
After reaching 7.04% in January, the average interest rate for a 30-year fixed mortgage has steadily remained in the mid-to-high 6% range. The 15-year fixed mortgage rate has hovered between the low-6% and mid-to-high 5% range since its January peak of 6.27%.
Rates have trended downward since mid-January 2025, but experts aren’t forecasting further significant decreases in 2025. Rate drops may continue in 2026, especially if the Federal Reserve continues to cut the federal funds rate down.
!function(){“use strict”;window.addEventListener(“message”,function(a){if(void 0!==a.data[“datawrapper-height”]){var e=document.querySelectorAll(“iframe”);for(var t in a.data[“datawrapper-height”])for(var r,i=0;r=e[i];i++)if(r.contentWindow===a.source){var d=a.data[“datawrapper-height”][t]+”px”;r.style.height=d}}})}();
When Can I Expect Mortgage Rates To Drop?
Mortgage rates are influenced by various economic factors, making it difficult to predict when they will drop.
Mortgage rates follow U.S. Treasury bond yields. When bond yields decrease, mortgage rates generally follow suit.
The Federal Reserve’s decisions and global events also play a key role in shaping mortgage rates. If inflation rises or the economy slows, the Fed may lower its federal funds rate. For example, during the Covid-19 pandemic, the Fed reduced rates, which drove interest rates to record lows.
A significant drop in mortgage rates seems unlikely in the near future. However, they may decline if inflation eases or the economy weakens.
How To Calculate Mortgage Payments
One of the first steps in buying a house is budgeting. To get a rough idea of how much owning a home will cost, start by using a mortgage calculator to crunch the numbers.
Just input the following data to get an idea of how much a house will cost:
- Home price
- Down payment amount
- Interest rate
- Loan term
- Taxes, insurance and any HOA fees
Find the Best Mortgage Lenders of 2025
How Are Mortgage Rates Determined?
Multiple factors affect the interest rate for a mortgage, including the economy’s overall health, benchmark interest rates and borrower-specific factors.
The Federal Reserve’s rate decisions and inflation can influence rates to move higher or lower. Although the Fed raising rates doesn’t directly cause mortgage rates to rise, an increase to its benchmark interest rate makes it more expensive for banks to lend money to consumers. Conversely, rates tend to decrease during periods of rate cuts and cooling inflation.
Home buyers can make several moves to improve their finances and qualify for competitive rates. One is having a good or excellent credit score, which ranges from 670 to 850. Another is maintaining a debt-to-income (DTI) ratio below 43%, which implies less risk of being unable to afford the monthly mortgage payment.
Further, making a minimum 20% down payment can help you avoid private mortgage insurance (PMI) on conventional home loans. If you can afford the larger monthly payment, 15-year home loans have lower rates than a 30-year term.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What is a good mortgage rate?
Average 30-year fixed mortgage rates land in the mid-6% range, so any rate at or below this range would be considered a good rate. However, several factors impact mortgage rates, including the repayment term, loan type and borrower’s credit score, so if you are considering applying for a mortgage, it’s a good idea to compare rates from several lenders to find the best rate for your situation.
Will interest rates ever go back to 3%?
The Federal Reserve’s efforts to stabilize the economy during the Covid-19 pandemic drove the historically low rates. As the economy recovers, the unemployment rate decreases and inflation is controlled, rates may dip below current levels, but they’re unlikely to fall as low as 3% again anytime soon.
What’s the difference between a mortgage interest rate and a mortgage APR?
A mortgage interest rate reflects what a lender is charging you on top of your loan amount in return for allowing you to borrow money.
Annual percentage rate (APR), on the other hand, is a calculation that includes both a loan’s interest rate and finance charges, expressed as an annual cost over the life of the loan. In other words, it’s the total cost of credit. APR accounts for interest, fees and time.
Since APRs include both the interest rate and certain fees associated with a home loan, the APR can help you understand the total cost of a mortgage if you keep it for the entire term. The APR will usually be higher than the interest rate, but there are exceptions.

Leave a Reply