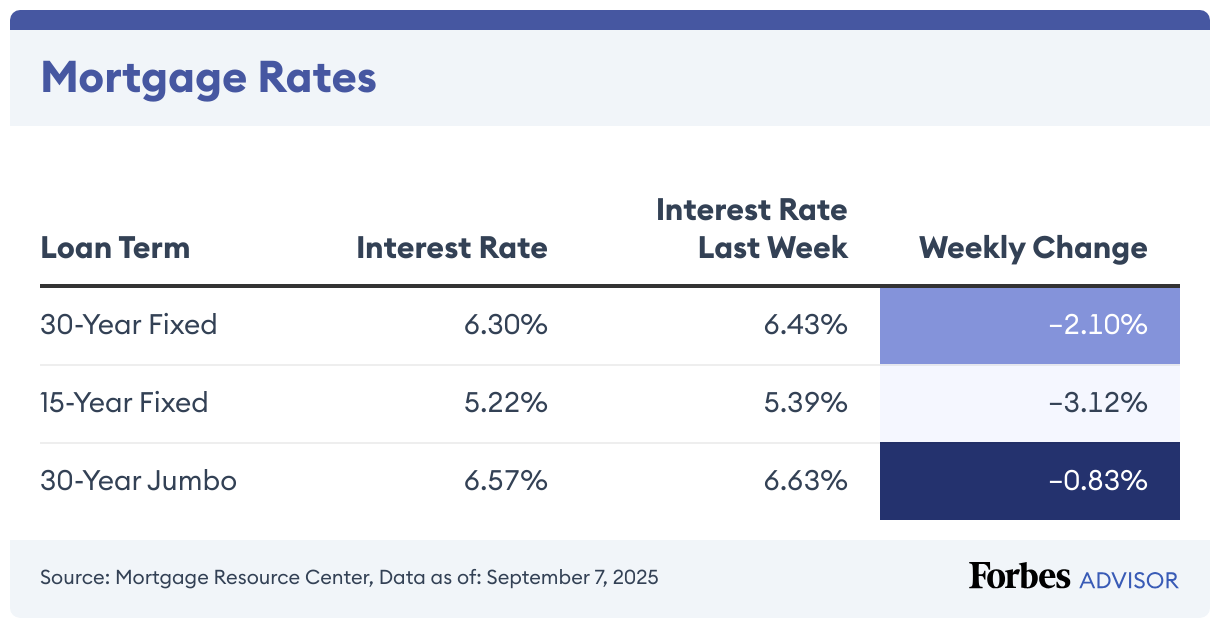
The current average mortgage rate on a 30-year fixed mortgage is 6.32% with an APR of 6.34%, according to the Mortgage Research Center. The 15-year fixed mortgage has an average rate of 5.45% with an APR of 5.49%. On a 30-year jumbo mortgage, the average rate is 6.68% with an APR of 6.70%.
30-Year Mortgage Rates Climb 0.64%
Today, the average rate on a 30-year mortgage is 6.32%, compared to last week when it was 6.28%.
The APR on a 30-year, fixed-rate mortgage is 6.34%. The APR was 6.31% last week. APR is the all-in cost of your loan.
With today’s interest rate of 6.32%, a 30-year fixed mortgage of $100,000 costs approximately $620 per month in principal and interest (taxes and fees not included), the Forbes Advisor mortgage calculator shows. Borrowers will pay about $123,864 in total interest over the life of the loan.
15-Year Mortgage Rates Climb 0.80%
Today’s 15-year mortgage (fixed-rate) is 5.45%, up 0.80% from the previous week. The same time last week, the 15-year, fixed-rate mortgage was at 5.41%.
The APR on a 15-year fixed is 5.49%. It was 5.45% a week earlier.
A 15-year, fixed-rate mortgage with today’s interest rate of 5.45% will cost $814 per month in principal and interest on a $100,000 mortgage (not including taxes and insurance). In this scenario, borrowers would pay approximately $47,018 in total interest.
Jumbo Mortgage Rates Drop 0.89%
The average interest rate on the 30-year fixed-rate jumbo mortgage (mortgages above 2025’s conforming loan limit of $806,500 in most areas) dropped to 6.68%. Last week, the average rate was 6.74%.
Borrowers with a 30-year fixed-rate jumbo mortgage with today’s interest rate of 6.68% will pay $644 per month in principal and interest per $100,000. That means you’d pay around $132,276 in total interest over the life of the loan.
Mortgage Rate Trends in 2025
After reaching 7.04% in January, the average interest rate for a 30-year fixed mortgage has steadily remained in the mid-to-high 6% range. The 15-year fixed mortgage rate has hovered between the low-6% and mid-to-high 5% range since its January peak of 6.27%.
Rates have trended downward since mid-January 2025, but experts aren’t forecasting further significant decreases in 2025. Rate drops may continue in 2026, especially if the Federal Reserve continues to cut the federal funds rate down.
!function(){“use strict”;window.addEventListener(“message”,function(a){if(void 0!==a.data[“datawrapper-height”]){var e=document.querySelectorAll(“iframe”);for(var t in a.data[“datawrapper-height”])for(var r,i=0;r=e[i];i++)if(r.contentWindow===a.source){var d=a.data[“datawrapper-height”][t]+”px”;r.style.height=d}}})}();
When Can I Expect Mortgage Rates To Drop?
Various economic factors influence mortgage rates, making it challenging to forecast when rates will drop.
The Federal Reserve’s decisions significantly impact mortgage rates. In response to inflation or an economic downturn, the Fed may lower its federal funds rate, prompting lenders to reduce mortgage rates.
Mortgage rates also track U.S. Treasury bond yields. If bond yields drop, mortgage rates typically follow suit.
Finally, global events that cause financial disruptions can affect mortgage rates. For example, the Covid-19 pandemic led to record-low interest rates when the Fed cut rates.
While a significant decrease in mortgage rates is unlikely in the near future, they may start to decline if inflation eases or the economy weakens.
How To Calculate Mortgage Payments
Mortgages and mortgage lenders are often a part of purchasing a home, but it can be tricky to understand what you’re paying for—and what you can actually afford.
Using a mortgage calculator can help you estimate your monthly mortgage payment based on your interest rate, purchase price, down payment and other expenses.
Here’s what you’ll need in order to calculate your monthly mortgage payment:
- Home price
- Down payment amount
- Interest rate
- Loan term
- Taxes, insurance and any HOA fees
Find the Best Mortgage Lenders of 2025
How Are Mortgage Rates Determined?
Home loan borrowers can qualify for better mortgage rates by having good or excellent credit, maintaining a low debt-to-income (DTI) ratio and pursuing loan programs that don’t charge mortgage insurance premiums or similar ongoing charges that increase the loan’s APR.
Comparing rates from different mortgage lenders is an excellent starting point. You may also compare conventional, first-time homebuyer and government-backed programs like FHA and VA loans, which have different rates and fees.
Several economic factors influence the trajectory of rates for new home loans. For example, Federal Reserve rate hikes indirectly cause the interest rates for many long-term loans to increase. Rates are more likely to decrease when the Fed pauses or decreases its benchmark Federal Funds Rate.
The inflation rate and the general state of the economy also impact interest rates. High inflation and a strong economy typically signal higher rates. Cooling consumer demand or inflation may lead to rate decreases.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What is a good mortgage rate?
Average 30-year fixed mortgage rates land in the mid-6% range, so any rate at or below this range would be considered a good rate. However, several factors impact mortgage rates, including the repayment term, loan type and borrower’s credit score, so if you are considering applying for a mortgage, it’s a good idea to compare rates from several lenders to find the best rate for your situation.
How long can you lock in a mortgage rate?
Most rate locks last 30 to 60 days and your lender may not charge a fee for this initial period. However, extending the rate lock period up to 90 or 120 days is possible, depending on your lender, but additional costs may apply.
What determines your interest rate?
National average interest rates depend on economic and market conditions, including the bond market, inflation, the economy and Federal Reserve decisions.
Lenders set rates based on the loan type and term. In general, shorter terms tend to come with lower rates. Additionally, making a larger down payment signals less risk to the lender, which could get you a better rate.
Other factors that can impact your rate include your credit score, debt-to-income (DTI) ratio, income and property location.

Leave a Reply